การเลือกชนิดของโบลวเวอร์
โบลวเวอร์เป็นพัดลมชนิดหนึ่ง ที่ใช้เพื่อเคลื่อนใหว (Air or gas movement) ถ่ายเทอากาศหรือแก๊ซจากที่หนึ่งไปอีกที่หนึ่ง ทำให้เกิดสุญญากาศ (Vacuum) เพราะอากาศหรือแก๊ซถูกดูดถ่ายเทออกไป โบลวเวอร์ใช้กันมากในกระบวนการผลิต และงานซึ่งต้องการบรรยากาศของสุญญากาศ
การเลือกโบลวเวอร์เพื่อให้เหมาะสมต่อการใช้งาน หรือเหมาะสมแก่การใช้งานในกระบวนการผลิต ต้องเลือกชนิด (Type) และขนาด (Size) ที่ต้องการ เพื่อให้ค่าใช้จ่ายในการลงทุน (Initial investment cost) และค่าใช้จ่ายในการใช้งาน (Operating cost) ต่ำสุด คือค่าใช้จ่ายตลอดวงจรการใช้งาน (Life cycle cost)ต่ำสุด โดยพิจาณาขีดความสามารถและข้อจำกัด ข้อดีและข้อเสียของชนิดโบลวเวอร์ที่เลือก
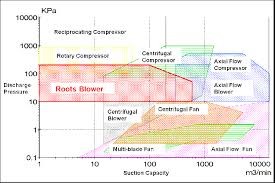
ชนิดของอุปกรณ์อัดความดันแก๊ซ (Difference type of gas mover)
แยกชนิดของอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนใหวอากาศหรือแก๊ซตามกำลังอัด (Classification With Respect to Compression Ratio)
| Type | Compression Ratio | Average Operating Pressure * |
| Fan | 0 – 1,3 | 0 – 0,25 bar |
| Blower | 1,1 – 2,5 | 0,15 – 2 bar |
| Compressor | > 2 | 3 – 12 bar |
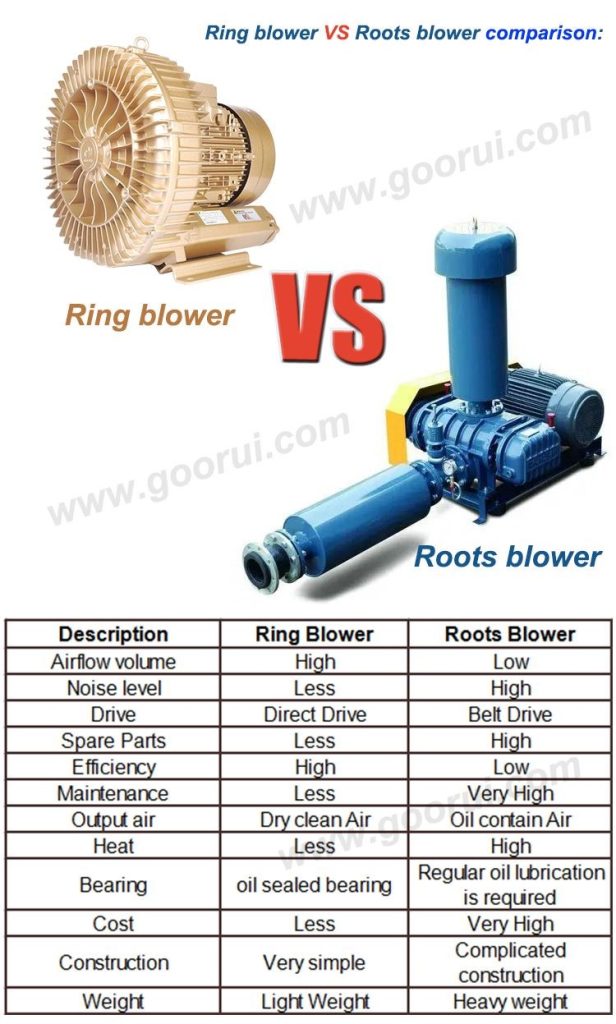
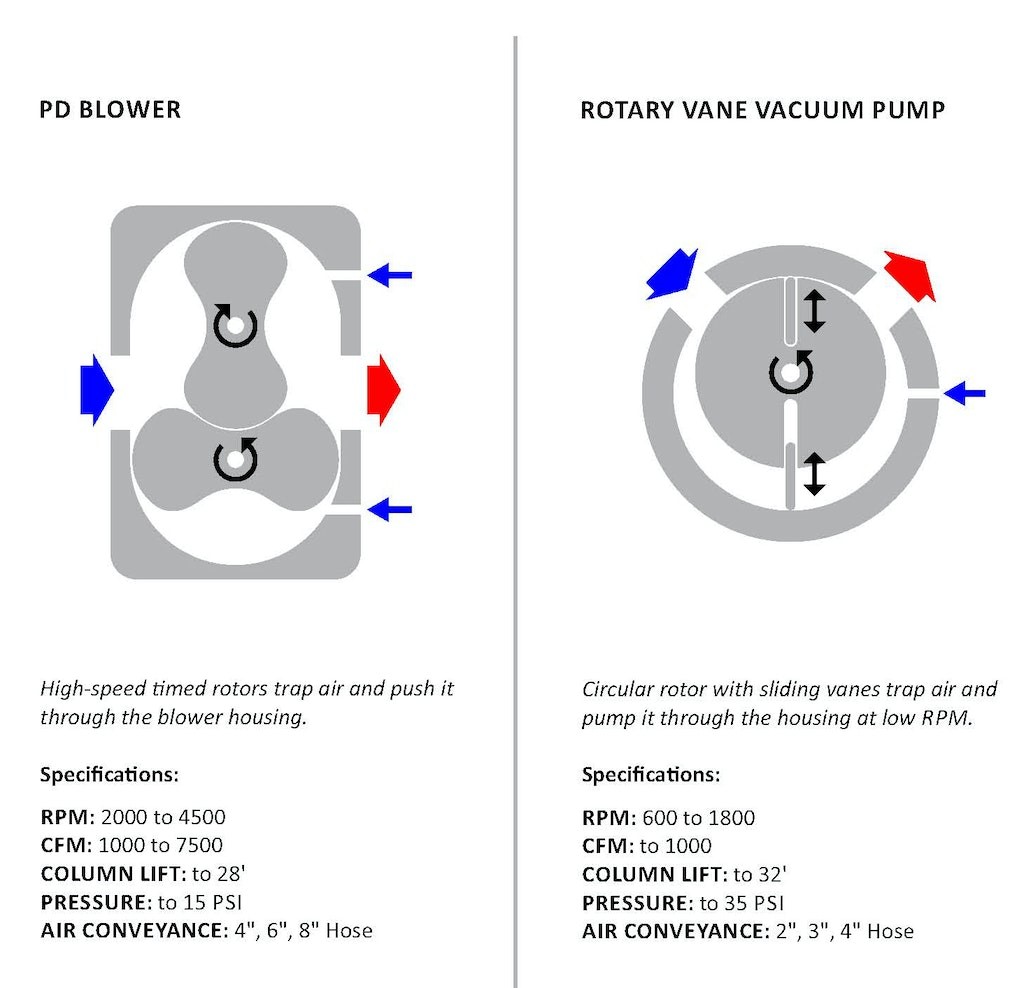
พัดลมกับโบลวเวอร์ต่างกันคือ (Difference Between Fan and Blower)
นอกจากคอมเพรสชั่นเรโช (Compression ratio คือ ความดันขาออกหารด้วยความดันขาเข้า) ที่ต่างกันแล้ว ข้อแตกต่างอื่นๆ เช่น
| Fan | Blower |
| Has blades for functioning or rotation | Has impellers for rotation |
| Is an electrical device | Is a mechanical device |
| It consumes less electricity | This relatively consumes more power |
| It offers medium airflow depending on the capacity | It offers better airflow than fans |
| Some types include radial fans, industrial axial fans, and propeller fans | The two main categories are centrifugal and positive displacement blowers |
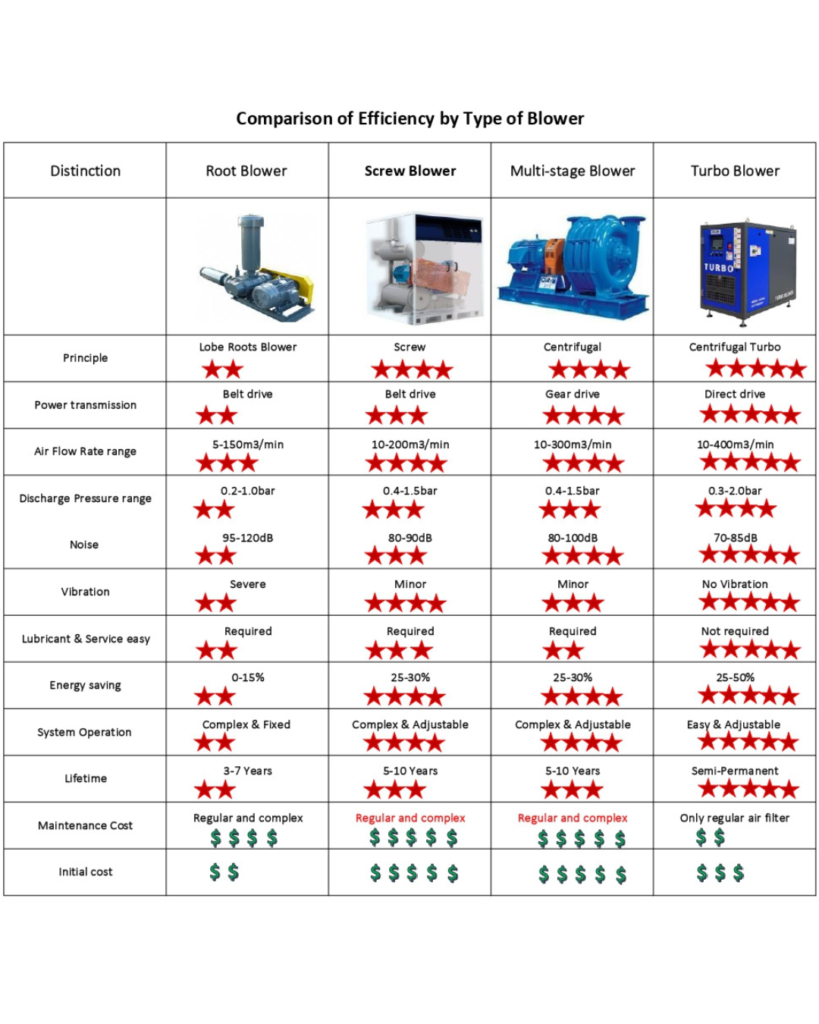
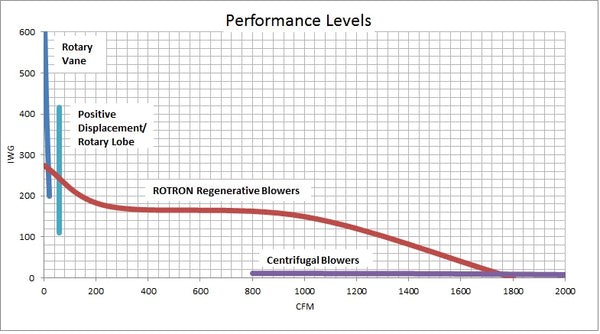
ตารางเปรียบเทียบคุณสมบัติที่ดีของโบลวเวอร์ (Blower Comparison Chart***) แต่ละชนิด และข้อจำกัด
| Flow, Pressure, Size* | Best Applications | |
| Centrifugal** | · Very low pressure – High flow
· Max. pressure 1 psi (27 inches W.C.) · Max. flow 1875 CFM · Weight 180 lbs |
· For applications where high flow at low pressures are required
· Blow off, heaters, ovens, tunnels |
| Regenerative** | · Low pressure – Medium flow
· Max. pressure 4.5 psi (125 inches W.C.) · Max. flow 420 CFM · Weight 321 lbs |
· For applications where moderate flows with significant pressure is needed
· Blow-off, heaters, ovens, tunnels · Appropriate for some vacuum applications such as conveyance and hold down |
| Rotary Vane | · High pressure – Low flow
· Max. pressure 22 psi (610 inches W.C.) · Max. flow 69 CFM · Weight 323 lbs |
· For applications where constant flow with variable pressure is needed
· Aeration, vacuum applications such as conveyance and hold down, vacuum pumps, compressors |
| Rotary Lobe | · Medium pressure – Medium flow
· Max. pressure 15 psi (415 inches W.C.) · Max. flow 100 CFM · Weight 88 lbs |
· For applications where constant flow with variable pressure is needed
· Aeration, conveyance, vacuum pumps · Oil-free motion makes it appropriate for food grade applications |
* All values are for 10hp blowers for ease of comparison.
** For centrifugal and regenerative blowers, the maximum pressure is reached at minimum air flow and vice versa. See our article on Flow, Velocity, and Pressure for more information.
*** Values are representative and may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer
ตารางเปรียบเทียบสมรรถนะระหว่างรูท สกรูคู่ และเซนตริฟิวกัลโบลวเวอร์
Comparison Between Roots, Twin Screw and Centrifugal Supercharger:
| S.no | Roots Supercharger | Twin-Screw supercharger | Centrifugal Supercharger |
| 1. | Powered by a belt driven from the engine crankshaft. |
It is also powered by a belt driven from the engine crankshaft. |
Centrifugal supercharger also gets power via belt or chain drive from engine crankshaft. |
| 2. | Working principle: Positive displacement type. |
Positive displacement type. |
Centrifugal type. |
| 3. | Fixed amount of air per rotation. |
Fixed amount of air per rotation. |
Not fixed amount of air per rotation. |
| 4. | Working: When two lobes turn in opposite direction, the air suction starts at fill side and pushes the same quantity of air at discharge side. |
Two same spiral rotors turn in opposite direction and both sides of gear pocket mesh together. Air flow at the inlet in auxiliary motion transported at discharge port compress as radially. |
Created force rotates the impeller at very high speed and it can suck the low-pressure air at the inlet and delivers the high-pressure air at the discharge port. |
| 5. | It makes much power in low rpm range. |
It also makes much power in low rpm range. |
Unlike root and screw supercharger it is good for high rpm range. |
| 6. | Least efficient. |
More efficient than the roots supercharger. |
Very much efficient. Almost same as turbocharger. |
| 7. | Less horsepower, Torque, and boost can be achieved. |
More horsepower, Torque and boost than the root but less than the centrifugal. |
Great horsepower, high torque, and more boost can be achieved. |
| 8. | Parasitic load: The device absorbs the crankshaft power to run themselves is more. |
Less parasitic load compared to roots type. |
Very less parasitic load is required. |
| 9. | Creates lot of noise. |
Less noisy than the roots type. |
Creates very less noise. |
| 10. | Creates lot of heat. |
Creates less heat compared to roots type. |
No Heating issue. |
| 11. | The construction is bulky and placed upon the top of the engine. |
Construction and design same as the roots type. This is also bulky. |
Small and compact. Placed in front of the engine. |
| 12. | Installation is difficult and some modification required in the inlet manifold. |
Installation is difficult but does not require extra modification. |
Easy installation. |
| 13. | Maintenance is required. |
Less maintenance compared to roots type. |
Less maintenance required. |
เปรียบเทียบการใช้งาน ค่าใช้จ่าย และการใช้พลังงาน ระหว่างโบลวเวอร์และคอมเพรสเซอร์
Applications, cost and energy management.
| Application | Air Compressor | Air Blower |
| Cleaning & Drying | Can be the best system if intermittent air bursts required. | Concentrated air flow, able to run continuously at low cost and with energy efficiency. |
| Blow-off | Ineffective at blow-off for certain industries. | Low pressure, high-velocity air flow suitable for blow-off applications. |
| Contamination | The cooling process needed to maintain compressed air means some fluid (oil and/or water) is ejected in the airstream, affecting drying applications. | Generates clean air - no air or oil needed in the system, meaning expelled air is dry. Able to create “air curtain” protective barriers. |
| Moisture regulation | High cost to run continuously, difficult to ensure precision needed for moisture regulation. | Air flow able to be easily directed, to create an “air curtain” laminar air flow that adheres to surfaces, meaning it can remove or regulate moisture on a surface as needed. |
| Large products | The size and energy requirements needed to deliver air over longer lengths are disproportionately large. | Easily supports large product drying/blow-off/moisture and contamination control. |
การเลือกโบลวเวอร์ต้องรู้ข้อมูลเบื้องต้น เช่น
- ชนิดและคุณสมบัติของของไหล
- ความดัน (ขาเข้าและขาออก)
- อุณหภุมิ (ขาเข้าและขาออก)
- ขนาดท่อ (ขาเข้าและขาออก)
- ลักษณะการใช้งาน (ต่อเนื่องหรือเดินๆหยุดๆ)
- ตัวขับเคลื่อน (มอเตอร์ หรือเครื่องยนต์)
- การติดตั้ว (อยู่กับที่หรือเคลื่อนที่)
การใช้งานของโบลวเวอร์ชนิดต่างๆ
เซนตริฟูกัลโบลวเวอร์
APPLICATIONS OF CENTRIFUGAL BLOWERS
Centrifugal blowers work for applications where low pressure air is required for some specific purpose. An example is when passing large air volumes in a furnace to fuel combustion. The required air volume is large, but does not need to be under pressure.
Major specific applications include:
- Climate control such as cooling, drying or maintaining temperature
- Exhausting or exchanging gases and vapours from one area to another
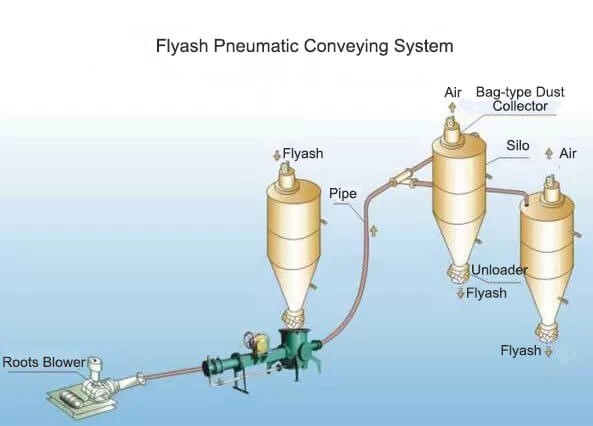
- Pneumatic conveying to transfer bulk powders or granules
Types of equipment and systems that use centrifugal blowers include:
- Filter and dust removal
- Furnaces and incinerators
- Grain elevators and silos
- Pneumatic conveying]
- Pollution control
Machinery that uses centrifugal blowers includes:
- Laminators
- Plastic extruders
- Printing
- Textile machines
- Woodworking
รีเจนเนอเรทีฟโบลวเวอร์
Applications of Regenerative Blowers
Regenerative blowers are generally used when a large volume of air at high pressure is needed for the specific application. They are also used in situations that involve flammable gas, or have some hazardous or heavy duty aspect to the process.
Major specific applications include:
- Pond aeration in aquaculture
- Sewage aeration in water treatment
- Soil vapour extraction in landfill sites
- Chip removal for engraving equipment
- Vacuum sintering and casting
Types of equipment and systems that use regenerative blowers include:
- Industrial vacuum
- Dust collector
- Pneumatic conveying
Machinery that uses regenerative blowers includes:
- Dryers
- Packaging
- Printing presses
- Spas
- Vacuum lifters
Pressure Roots Blower Application
There are many industrial pressure roots blower applications. These range from assisting in combustion by pumping air or gas into burners, furnaces and forges to pressurising paper mill head boxes. The following are some typical examples.
Combustion
Used in the following industries:
- Bricks
- Bakeries
- Chemical
- Glass and ceramics
- Food processing
- Metal refining
Applied to equipment such as:
- Asphalt, oil, and tar heaters
- On-road machinery
- Ovens and kilns
- Pipe and wrapping machines
- Smelters and foundries
Drying and Dehydration
Used in the following process:
- Air and sandblasting
- Dust and cake blowing
- Dusting and spraying
- Grain conditioning in elevator storage
- Blending and mixing
- Sand filter regeneration
- Supercharging
- Washing and drying drums
Aerating and Agitation Liquids
Used in the following process:
- Asphalt refining
- Blending vinegars
- Chemical processes
- Electrotyping and engraving
- Flotation
- Fish ponds and lakes
- Food washing
- Ice manufacture
- Ice formation prevention
- Oyster washing
- Waste treatment
Pneumatic Conveying
Used in transporting the following materials:
- Granules and extruded materials
- Flour, dusts and powders
- Liquids and pulp
- Wood and metal chips
Vacuum Roots Blower Application
Roots blowers are frequently used as vacuum pumps in dust collecting and drying processes. Industrial vacuum roots blower applications are, however, widespread and include specific industrial processes such as:
- Bottle and tube filling machines
- Garment presses and mechanical mat formers
- Industrial and commercial vacuum cleaning
- Paper folding machinery
- Pump priming
Conclusions
- The mechanical technology for air compression has existed for more than a century.
- The breakthrough nowadays is on the minimization of transmission losses hence the improvement of efficiency.
- The degree of maintenance is also improved as the result.
- To select or enquire for a blower, the wider issues such as air cleaning, turndown, efficiency, air
- temperature & humidity, noise and key cost contributors shall be considered.
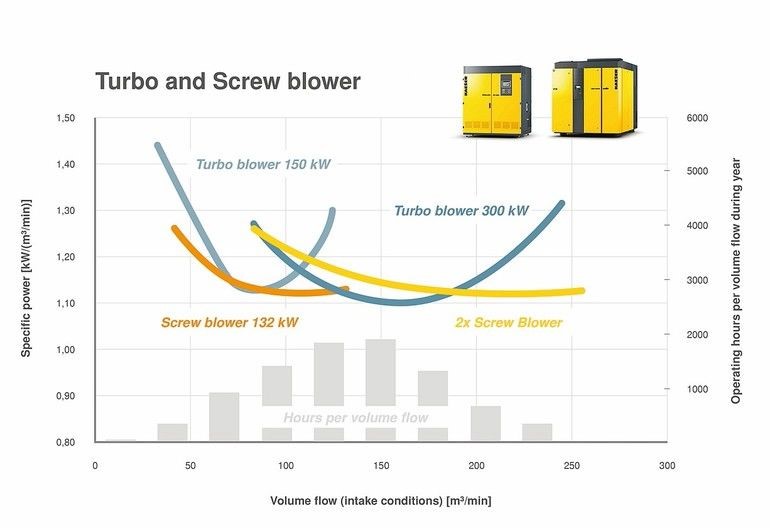
- The rotary lobe blower is the strong contender for application below 2000 Nm3/hr provided the turndown is achievable.
- The high speed turbo blower offers the smallest footprint for majority of air flow rates.
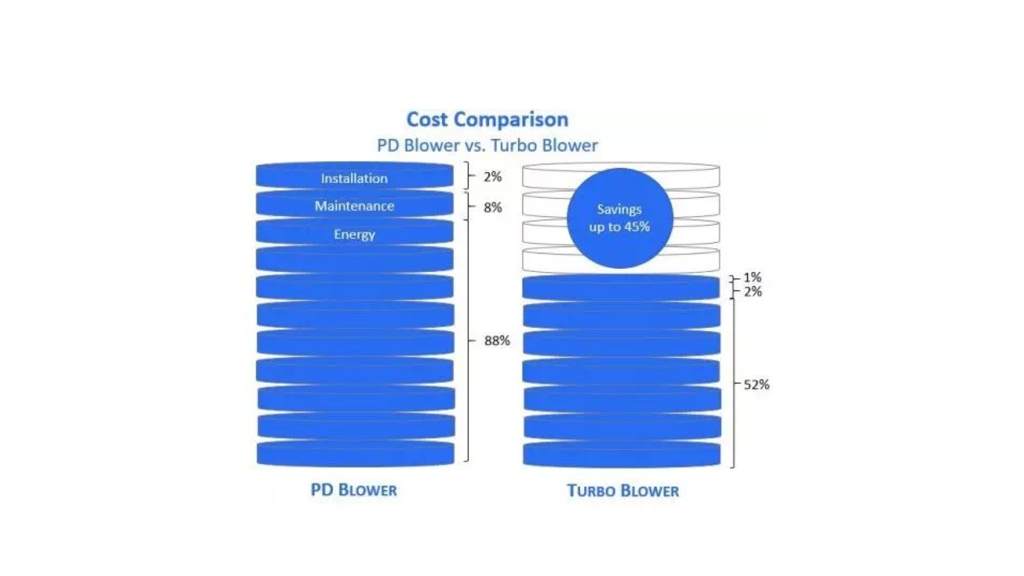
- The unit cost of blower increases exponentially as the air flow rate increases. The difference in unit cost
- between different blower types and installation related costs could be paid back within 10 years of operation.
- The maintenance cost which consists of both the preventative maintenance and replacement parts including labour is minimal in comparison with the electricity cost in the long run.
- The conventional centrifugal blower remains the technology which covers the widest range of air flow duty.
This paper and the associated results are subject to the following limitations;
- The equipment data is based on the information provided by the selected reputable vendors and may not represent all the blowers available on the market. It is strongly encouraged that the designer or asset owner carries out own assessments during the design or procurement processes.
- No external or third party verification has been carried out on the data given.
- The comparisons in this paper have focussed on single operating blower unit. The results may not be applicable to multiple units in operation.
- The maintenance cost data provided by the vendors can subject to interpretation errors and potentially commercial bias. For better and more accurate results, the cost is to be studied at “skeleton” levels.
บริษัทไอคิวเอส เป็นผู้แทนจำหน่ายโบลวเวอ์เกือบทุกชนิดจากแบรนด์ชั้นนำระดับโลก เช่นของพีเอสจี โดเวอร์ (PSG Dover) ซูวอน (Suewon) เอฟพืแซด (FPZ) เคเอฟเอ็ม (KFM) เป็นต้น ซึ่งเป็นแบรนด์ชั้นนำ มีใช้งานอย่างแพร่หลายในอุตสาหกรรมทั่วโลกและในประเทศไทย
บริษัทไอคิวเอสมีวิศวกรที่มีความรู้ ความชำนาญ และประสบการณ์เพื่อให้คำปรึกษา ในการเลือกชนิด (Type) ขนาด (Size) และกำลัง (Rating) ของโบลวเวอร์ที่เหมาะสมแก่การใช้งาน และได้รับการสนับสนุนทางเทคนิคจากบริษัทผู้ผลิตโดยตรง
บริษัทไอคิวเอสมีโบลวเวอร์ให้เลือกหลายแบบ หลายขนาด หลายวัสดุ หลายวัสดุตามแต่การใช้งาน มีหลายแบรนด์ และหลายราคา
สนใจสินค้า ขอคำปรึกษา ติดต่อ บ. อินทีเกรทเต็ด ควอลิตี้ เซอร์วิสเซส จำกัด